LACTOSE INTOLERENCE
The following is a review on a paper I read up on titled : “Systemic lactose intolerance: a new perspective on an old problem” by S B Matthews, J P Waud, A G Roberts, A K Campbell.
The body’s intolerance to various types of foods can result in an range of different gut and systemic symptoms.
The ability to determine that these has been as a result of lactose has been overlooked and not recognised due to various food and drink manufacturers secretly adding lactose and refraining from labelling that it contains it . Thus causing a confusion with respect to diagnosis on dietary removal of the respective dairy foods .
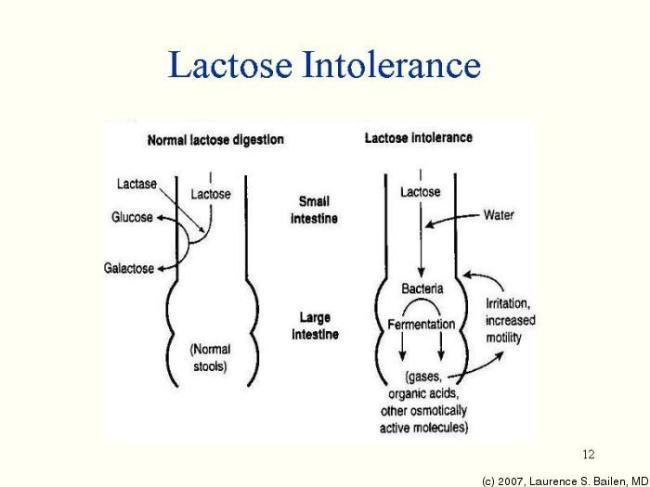
Lactose Intolerance, commonly known as milk intolerance or dairy product intolerance, is an inability to digest lactose in small intestines. Lactose, a type of discharide sugar consisting of galactose bound to glucose, is commonly found in milk and other dairy products. The absorption necessitates the hydrolysis of lactose to it’s components by the enzyme lactase. This is the enzyme not present or the absorption does not occur correctly in those with lactose intolerance .
The cause Lactose intolerance is very common among people. The cause is the deficiency of lactase and it is because of both genetic and environmental induced factors. I myself suffer with this problem L that is why this research paper was rather useful and informative to me . Not only did it apply to me on a personal level , but I aided me in understanding the topic much better .
They also pointed out the significance in being able to differentiate between hypolactasia, a low level of lactase, and clinical lactose intolerance. (I had no idea about this ) It goes on to describe the mechanisms causing lactose intolerance , which is the unique enzyme called lactase . (this I knew already ). However I did not know there were in fact three causes of loss of lactase (hypolactasia) which are :
- Congenital complete loss of lactase (very rare).
- Inherited loss, after weaning (common).
- Secondary intestinal damage, for example, infections such rotavirus and Giardia, or hormonal imbalance.
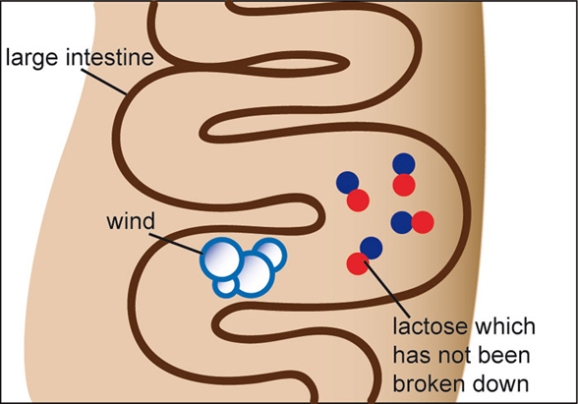
When lactose reaches bacteria in the hypoxic large intestine, hydrogen and other metabolites are generated.
The condition Lactose intolerance was initially detailed and described by Hippocrates. Despite his recognition of this long ago it is only within the last 50 years that this condition been documented , acknowledged and diagnosed medically
The paper also indicated that patients who suffer with lactose intolerance must also be advised of something they refer to as risk food .As a result of manufacturers inadequate labelling and negligence in mentioning the lactose in their products . Some examples of such food products are processed meats, bread, cake mixes, soft drinks, and lagers. This was very shocking to me :o. I really and truly did not know this and I am pleased to have stumbled upon this research paper. Therefore in the future I would be weary of what I eat , I now understand my frequent gas issues , flatulence and upset stomach .
On completion of reading this paper I was able to deduce that lactose can cause a range of debilitating systemic symptoms, as well as the renowned gut symptoms.
Postgrad Med J 2005;81:167-173 doi:10.1136/pgmj.2004.025551
Systemic lactose intolerance: a new perspective on an old problem
S B Matthews1, J P Waud1, A G Roberts2, A K Campbell3
+ Author Affiliations
1Department of Medical Biochemistry and Immunology, Llandough Hospital, Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust, Penarth, Vale of Glamorgan, UK
2Department of Medical Biochemistry and Immunology, Cardiff and Vale NHS Trust, Cardiff, UK
3Department of Medical Biochemistry and Immunology, Wales College of Medicine, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK
Correspondence to: Professor A K Campbell Department of Medical Biochemistry and Immunology, Wales College of Medicine, Cardiff University, Heath Park, Cardiff CF14 4XN, UK; campbellak@cf.ac.uk